RAIC SYLLABUS
THESIS PROJECT
2005
INTRODUCTION
TO
ARCHITECTURAL
DESIGN
Kurt Dietrich
SK85ON23
June 2004
ARCHITECTURE
Architecture is the art and science of designing
buildings. The practice of architecture includes design from the macro-level of
the total built environment (civic centers, subdivisions, urban planning and
landscape design) to the micro-level of furniture and product design.
In
300 a.d., a Roman writer named Vitruvius created "The Ten Books on
Architecture" covering all aspects of design and community planning as
well as military and social design elements.
He notes that a good building should have Beauty (Venustas), Firmness
(Firmitas) and Utility (Utilitas). True
architecture should present a balance of these three elements. The role of
architectural design in current times also includes the responsibility to
resolve functional, aesthetic and psychological considerations of the intended
users.

Pisa Cathedral,
Italy
The
practice of architecture is a multi-disciplinary profession integrating the
skills of mathematics, science, art, technology, social sciences, politics,
history, geography and philosophy.
Philosophy is key component in the analysis of an architect's
practice. It is the philosophy of the
practice that defines the rationale by which they produce particular solutions
to definitive problems. Rationalism, empiricism, structuralism, post-modernism,
deconstructivism structuralism and phenomenology are some directions from philosophy
influencing architecture.
The general public should be given the opportunity to understand that Architecture touches our lives in every way by the manner in which we exist and present ourselves through our buildings. Architecture influences all facets of daily lifestyle.
This thesis
intends to address the public perception of Architecture through an educational
setting. The thesis process begins with
development of an educational curriculum for the purpose of instruction in
architectural design principles. This
curriculum will be developed in consultation with practicing educators. The curriculum will be developed during the
research stage until it is deemed completed by the participating educators.

Stonehenge, Salisbury Plain, England
ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN EDUCATION
The goal of education in architectural design principles is to cultivate the creativity in a person who contributes to improvement of architectural culture and growth.

The Colusseum, Rome, Italy
Architectural design provides a distinction between existence and living. The basic requirements of structures include shelter and arrangement of space, both of which are utilitarian. The additional feature provided by architectural design is that of aesthetics, the expression of a building. All three items; shelter, arrangement and aesthetics must be seamlessly integrated in order to achieve a successful architectural solution.
Architecture is created by using the tangible requirements for shelter and proper arrangements put through a design process to provide a solution capable for the expression of a defined lifestyle, aesthetically practicing specific values. The medium of the art of architecture is found in the masonry, wood materials, metals, glass and concrete. The use of these media produces the interior spaces and exterior appearance of our great buildings.
The architectural profession assumes the role of educator on every project. The role of the Architect is to analyze the problem, explain the process, propose and carry out implementation of the design solution and educate the client relative to the proposed solutions. This process of education is present from a simple roof design through to the most complex urban planning solution.
This thesis will create opportunity for awareness and understanding of the built environment. The aim of the education curriculum is to encourage a positive development of attitude and approach towards architecture and the built environment. This aim is achieved through increasing awareness and understanding of architecture in our youth. Achievement of this aim will provide participants with an understanding of “reading architecture” in their everyday lives.

The Pantheon, Rome, Italy
Buildings and exterior spaces affect us all the time, no matter where your location. The influence can be felt through experience of the building and courtyard or plaza. The experience is felt through the method of arrival, circulation or traveling through the building, lighting on both exterior and interior, views, textures, colours and details. These subtleties are typically invisible to most of us in our daily lives. Architectural buildings and spaces create an environment that always provides something new, something comforting, and something tangible. Architecture is man made and thus, we have control over how we create and live in our selected environments

The Pantheon, Rome, Italy
CURRICULUM COMPONENT DEVELOPMENT
The parameter applied to the educational delivery process involves elementary grades seven and eight students coming to the proposed facility for one afternoon each week during a single reporting period of the standard school year. A single reporting period allows for 16 instructional sessions. The research development will complete a breakdown of 16 units related to the curriculum structure.

The Parthenon, Athens, Greece
Grades Seven and Eight are the proposed target group. Students in this age group, ages 12 – 14 years, are in the process of identifying their personal space and role within the community. They are developing a greater awareness of themselves relative to the world around them. This age period is a stage of personal and social growth. It is a time for individual exploration in the environment. These grade levels demonstrate capabilities which allow them to perceive three dimensional constructs and grasp conceptual ideas. These grade levels have the language skills necessary to discuss concepts and ideas relative to architecture and design.
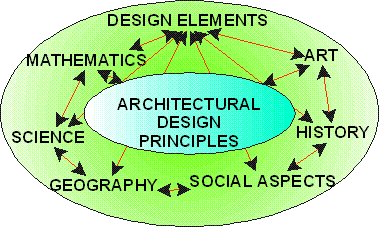
The basis for the curriculum components of this thesis will follow a consistent breakdown of elements for each educational item. A summary of the proposed educational components to be reviewed relative to architectural design principles includes:
· Design Elements
· Mathematics
· Science
· Geography/Geology
· Social Aspects
· History
· Art
All of
these items are interrelated in the process of architectural design. Overlaps between sections will likely
occur. Where possible, these overlaps will
be identified in the educator resource materials to allow for reinforcement of
the principles relative to the specific section and related sections.
The
breakdown for each curriculum component will be:
EDUCATIONAL COMPONENT:
{Name of educational section}
ABSTRACT:
{Definition
of architectural relevance}
PREAMBLE:
{General course outline, course extent, etc}
COMPONENT
INTIATIVE:
{Goals for providing this component: what do we hope to achieve
through the instruction}
COMPONENT COURSE
MATERIALS:
{The
instructional meat of the course}
- Explanation
of relevance to architecture
- full text on
the course materials
- background
- reasons for
learning
- applications
to instruction
- relevance to
architectural design
- future use
strategies}
INSTRUCTIONAL
STRATEGY:
Fixed
options will be expanded upon}
·
Direct
Instruction
·
Indirect
Instruction
·
Experiential
Learning
·
Independent Study
·
Interactive
Instruction
ACTIVITIES:
{Student
activity listing for participating in the class}
·
Oral
·
Visual
·
Kinesthetic
·
Written
ASSESSMENT
METHOD:
{Proposed
assessment method for student performance and retention evaluation}
·
Pencil &
paper method
·
Performance
assessments
·
Personal
assessments
COMMON ESSENTIAL
LEARNINGS:
{Description
of how this educational component fits to the listing of Common Essential
Learnings}
·
Communication
·
Creative and
Critic al Thinking
·
Independent
Learning
·
Numeracy
·
Technological
Literacy
·
Personal &
Social Values & Skills
ENVIRONMENT:
{Type of environment
required to suit the instructional and student methods outline}
·
Classroom Climate
·
Physical Setting
·
Flexible student
groupings
·
Extensions beyond
classroom setting
·
Community
experiences
MATERIALS /
RESOURCES REQUIRED:
{Listing of
required materials for both educator and students participating in the
component}
·
In-room supplies
·
External supplies
NEW TEXT
DEFINITIONS:
{A listing
of new architectural definitions provided by this component}